CHARGE AIR COOLING AND AIR COOLERS ON SHIP
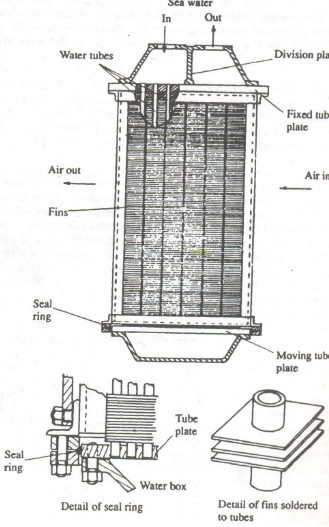
Charge Air Cooling : The air density determines the maximum weight of fuel that can be effectively burned per working stroke in the cylinder, it also determines the maximum power that can be developed by the engine. The increase in air density is fractionally offset by increase in air temperature resulting from compression by turbochargers. Much of this potential loss can be recovered by charge air coolers. Charge air cooling has double effect on engine performance : By increasing the charge air density it increases the weight of air flowing in cylinder and by lowering the air temperature it reduces maximum cylinder pressure, exhaust temperature and thermal loading. Air Cooler : The most common type of cooler is water cooled design with finned tubes in a casing carrying sea water over which the air passes. For efficient cooling velocity of air should be low and cooling area large. This is obtained by making air inlet connection divergent and outlet is convergent t...




